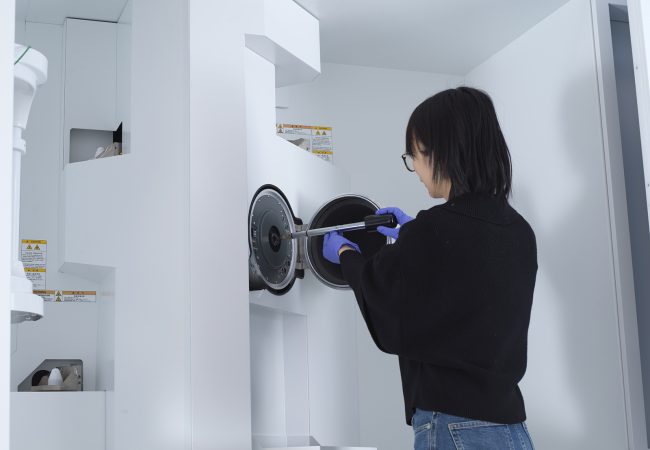

New electron microscopy method opens window into structural studies of thicker, more complex biological samples
Scientists at the Rosalind Franklin Institute have demonstrated a novel way to recover high-resolution structural details of biological objects using transmission electron microscopy – a technique that could reveal new details from thicker, more complex specimens than before. The approach,…
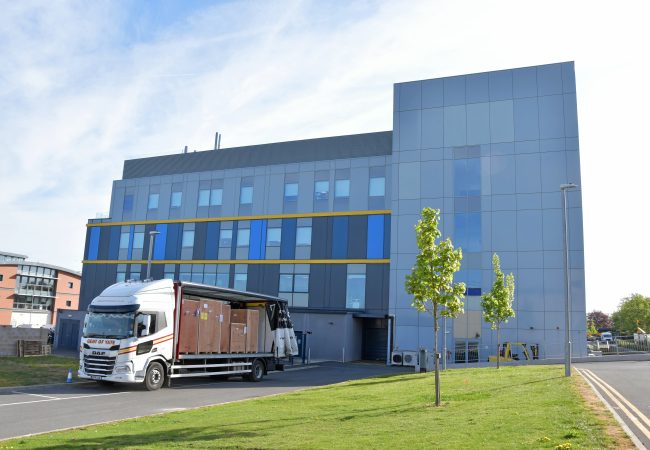

New cutting-edge microscope for the UK
The UK’s first Chromatic Aberration-Corrected Electron Microscope has arrived at the Rosalind Franklin Institute. This state-of-the-art instrument will significantly enhance the resolution limits for biological sample imaging, especially for thicker specimens. This delivery marks the final instalment of three advanced…
BioCOP – the UK’s first multimodular optical microscope – enters testing phase
Biophotonic Correlative Optical Platform (BioCOP), which is located at the Rosalind Franklin Institute (the Franklin), has entered its next phase of development of calibration and benchmarking. The instrument is now assembled, and the team will start testing it with model…

Angus Kirkland
Angus is Science Director at the Rosalind Franklin Institute, professor materials and Electron Microscopy at University of Oxford and the electron Physical Sciences Imaging Centre at Diamond Light Source. His research interests include the development and applications of aberration corrected…
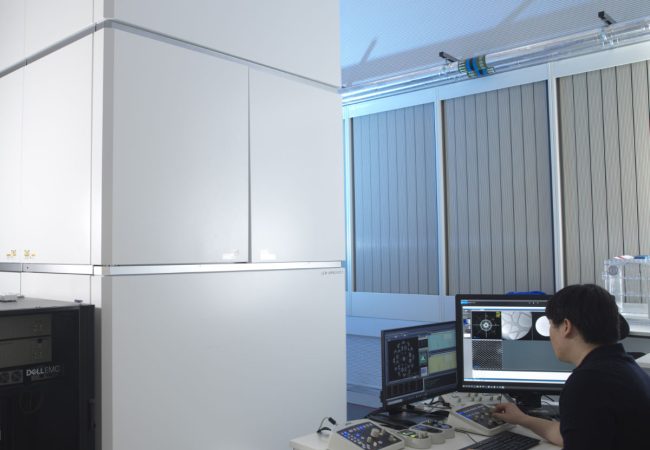

Aberration-corrected transmission electron microscope
Ruska is an aberration-corrected transmission electron microscope (TEM) used to explore novel methods to study radiation sensitive specimens such as biological materials that have been cryogenically preserved or encapsulated in liquid for dynamic observations.
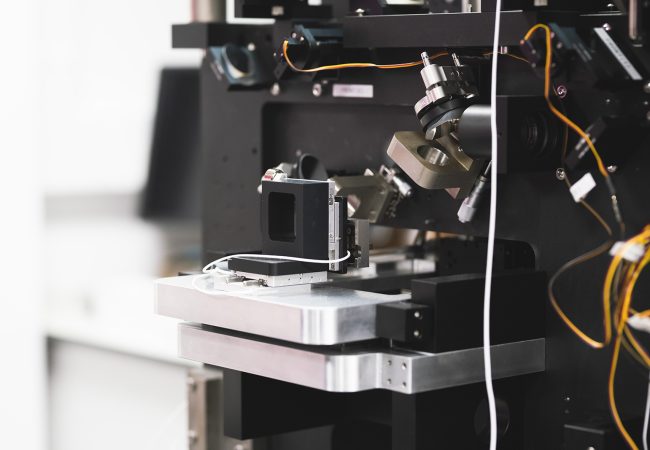

BioCOP
The BioCOP: ‘pushing the boundaries’ of biological imaging across space and time.
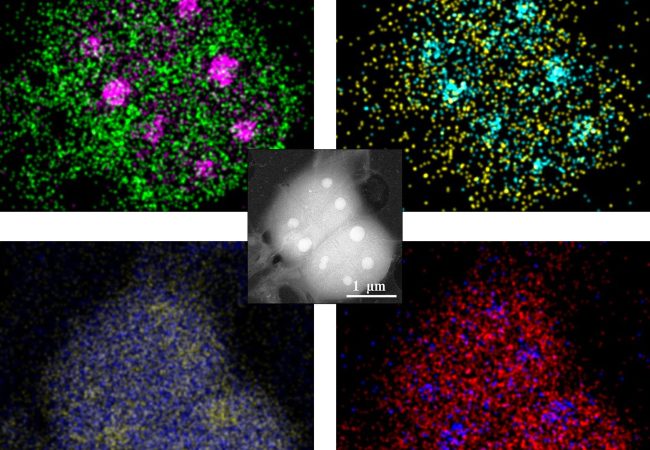
Liquid Phase Electron Microscopy and Spectroscopy
Transient, dynamic assemblies of biomolecules in solution are the primary driving forces behind biology. However, studying these at high resolutions requires the use of electron microscopes (EM), which need extremely high vacuums to function.
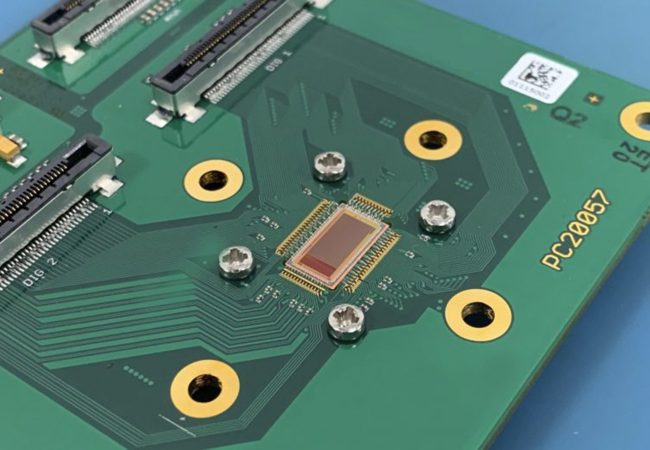

Electron Detector Development
Atomic resolution imaging with electrons causes sample damage. The information per unit of damage is dependent on sample thickness and beam energy.
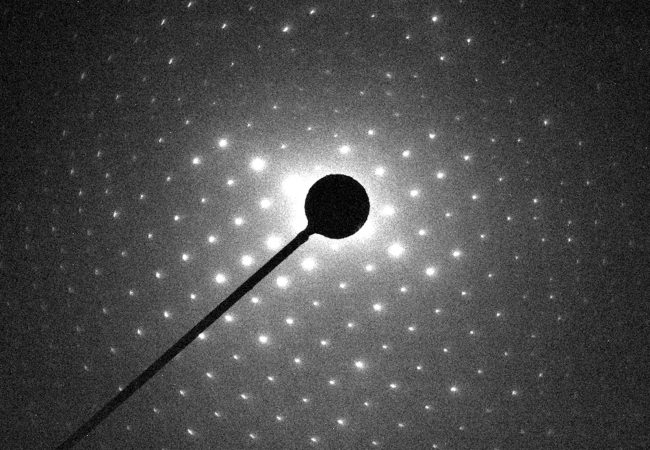

Electron Diffraction
MicroED is an emerging technology that exploits the strong interaction of electrons to reveal the structures of molecules from vanishingly small crystals.
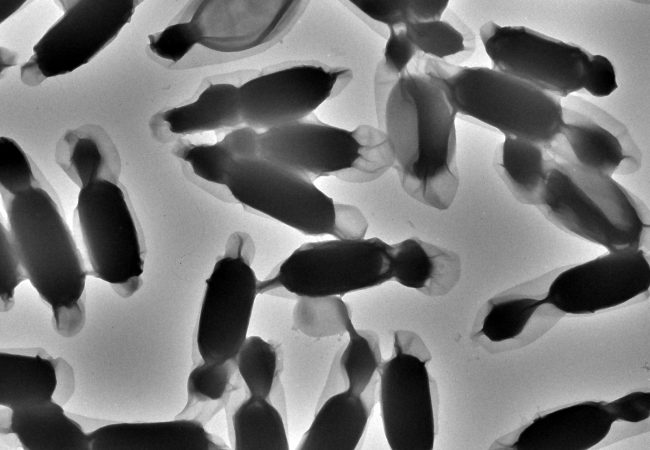
Cryo-ptycho-tomography
Developing a novel technique using cryo-electron ptychography to perform tomographic characterisation of biological processes at cellular scales, enabling detailed study of rare and complex structures in their native environments.
