Improved plasma-based imaging technique paves way for higher-resolution analysis of health and disease
A multidisciplinary team of scientists has shown, for the first time, that a microscopy technique called cryo-plasma FIB/SEM can produce high-quality volumetric information of natively preserved biological samples, precluding the need for fixation or resin embedding. This paves the way…
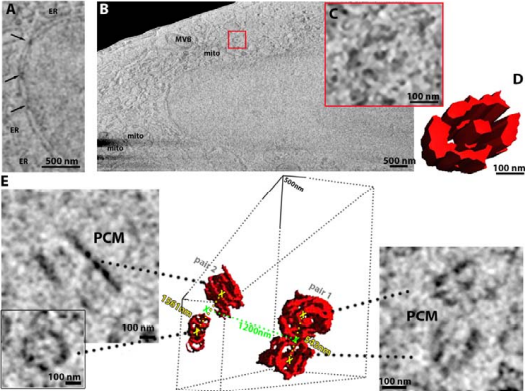
A new approach that advances the field of electron cryo-tomography
Rosalind Franklin Institute researchers, working with Thermo Fisher Scientific, have developed a new approach that advances the field of electron cryo-tomography. This plasma ion sources for sample preparation required for in situ structural biology electron cryo-tomography and enables future studies into sample…

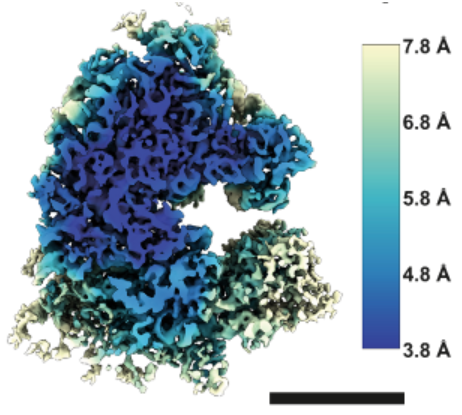
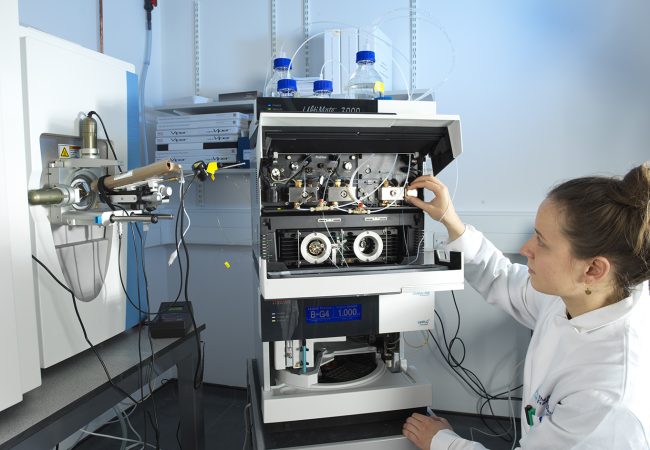
A new and unique mass spectrometry instrument has arrived at the Rosalind Franklin Institute
A new and unique mass spectrometry instrument has arrived at the Rosalind Franklin Institute as a part of our collaboration with the instrument manufacturer, Bruker. The instrument is designed to be a precision tool for the structural study of biomolecules.…
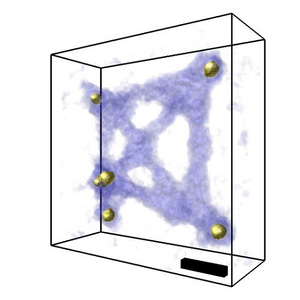
New simplified methods for imaging DNA nanostructures
DNA nanostructures can be changed and improved using different biological and chemical processes, allowing them to be used more accurately in applications such as drug delivery. As a result, imaging functional and multidimensional DNA nanomaterials is important in a range…
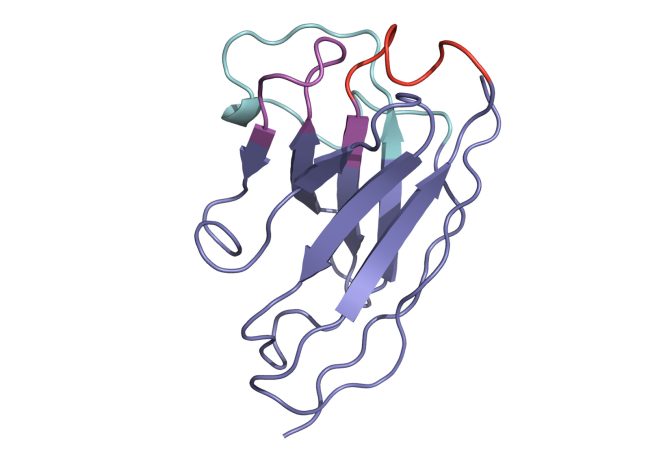
Lab-derived nanobodies move closer to being potent addition to pandemic toolkit
The rapid development of nasal sprays to treat future respiratory viruses is a ‘real possibility’ after scientists showed how to use structural insights to improve the potency of lab-derived nanobodies against Covid-19. The team had previously demonstrated that nanobodies – a…
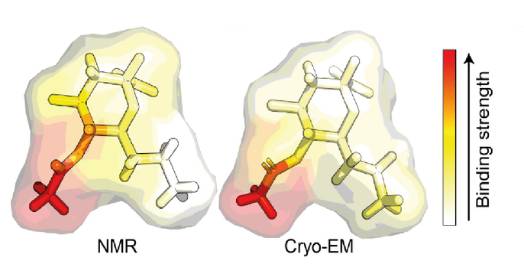
Discovery of new Covid infection mechanism offers clue to SARS-CoV-2 leap to humans
One of the best-known aspects of the Covid-19 pandemic is that the virus ‘jumped’ into people from animals – perhaps bats or pangolins – in a process known as zoonotic transfer. What hasn’t been clear to scientists is exactly how,…

Scientists find new way of ‘chopping’ proteins chemically
A team of researchers from the Rosalind Franklin Institute and Oxford University has discovered, using cheaply available reagents, a novel and simple way of breaking down proteins by targeting a particular chemical bond. The new method appears to mimic an…
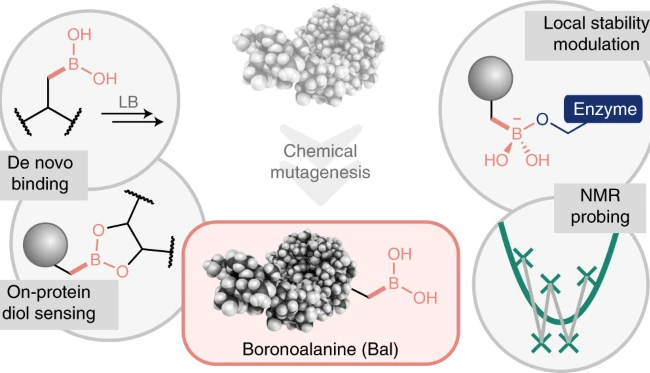
Introduction of boron to proteins could pave way for expanding biological function
A new study by scientists at the Rosalind Franklin Institute explores the role of boron in biology, revealing a host of uses for a chemical element that is little-studied in this context. While boron has long been acknowledged as a…
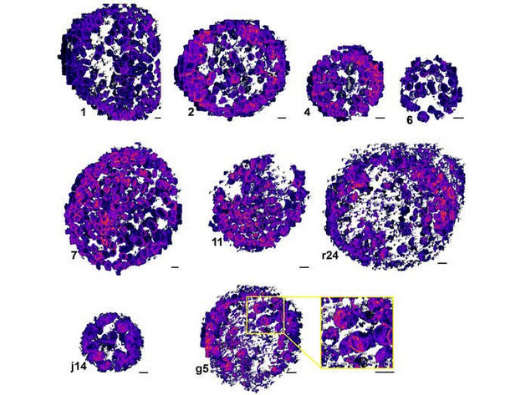
High-res imaging reveals organisational behaviour of chlamydia-causing bacteria
A powerful new imaging technique has helped researchers shed light on an important class of bacteria responsible for a range of diseases in humans and animals. Best known as the cause of a sexually transmitted infection, Chlamydiae are a diverse group of…
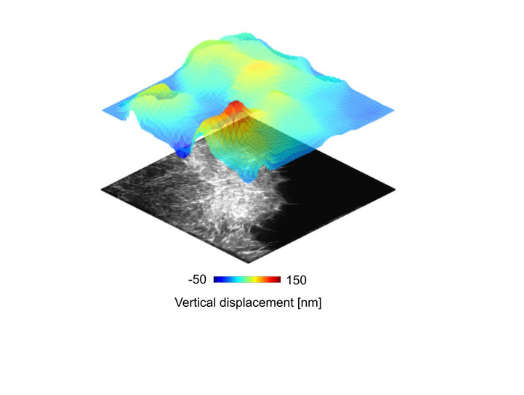
Researchers measure small forces inside immune cells using advanced microscopy
Scientists from the Rosalind Franklin Institute and the Kennedy Institute at the University of Oxford have, for the first time, measured the small mechanical forces generated by cells during an immune response. Using a combination of advanced microscopy techniques, the…
